# WX Network Protocol
# Motivation
The need to convert and exchange tokens is increasing with the growing number of crypto currencies. One of the main features of the blockchain environment is decentralization, but until recently only centralized exchanges existed, even for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. Many exchanges support buying and selling cryptocurrencies, fiat currencies, and cryptocurrency tokens. Examples of such centralized exchanges are Coinbase, BTC-e, ShapeShift and Mt.Gox. The centralization experience in this sphere is lamentable, the cause of a single point of failure - the exchange. In this case, all users funds should be kept in one place for participation in trade. The user's funds are stored directly in the exchange, and it is responsible not only for matching orders and keeping the current order book in the correct state but also for depositors' funds. The Mt.Gox collapse is the brightest example of why it is not reliable, the resulting loss after being compromised was about 650,000 BTC. Someone can hack into exchange system and all users will lose everything, because their private keys are kept all together, like in one of version BTC-e fund's theft. And these are not the only exchanges that have lost the funds of depositors this way. The decentralized approach of an exchange helps to avoid the involvement of many user tokens into problems caused by the danger of front running by intruders into the work of exchange.
# Decentralized Exchange
The decentralized exchanges do not require users to trust them with their money: user's wallet is not controlled by a single entity. Orders are digitally signed directly by owners, as an authorization process. Users control their funds, but on-chain trading has the side effect of trading not in real-time as at a centralized exchange.
Decentralized exchanges have some advantages over centralized, but also the drawbacks.
If all the components of the exchange are decentralized there is no automatic matching of buy and sell orders, these operations also should be done by users. For example, for a specific order, which is validated and put in an order book, any other user can add a digitally signed counterorder and send the complete transaction with a pair of orders to the blockchain. Then the tokens are transferred between the buyer and seller.
Also with such lack of automatic matching and fast cancellation, there is vulnerability to miner front-running. The miner of the next block will always have the option to execute canceled orders with themselves as the counterparty, potentially profiting from such an order.
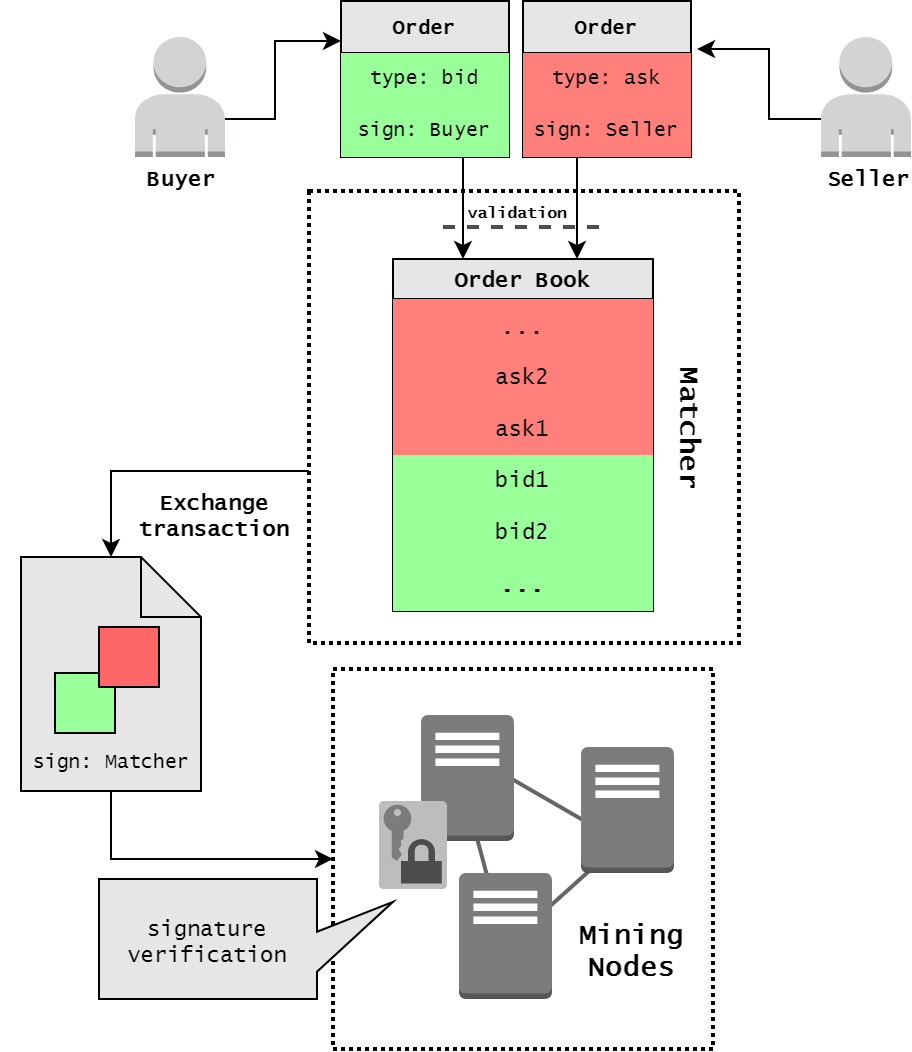
What if we decentralize not all components of exchange, but only the matcher part? This design eliminates two of the described problems above: the arbitrageur with already canceled orders, and miners front-running. Unlike centralized exchanges, the decentralized solution with centralized matcher won’t have the power to steal users’ deposits.
# WX Network
WX Network provides a decentralized exchange, which allows trading different tokens back and forth between users, as a traditional exchange, with stronger security guarantees to end users due to its decentralized nature. An opportunity of creating some new tokens, based on Waves, allows early trading of a crowdfunding stake, that provides liquidity for tokens. For this purpose, tokens should be sold in public locations, where buyers and sellers may post orders.
The real-time trading is achieved thanks to the only centralized design element of our WX Network - the order book Matcher, which matches incoming orders and executes trades at high speed, typically within milliseconds. There is no need to wait for the next block to know whether a trade has been executed successfully. This provides speed at the level of centralized exchange and the security of the decentralized protocol.
The orders are linked in pairs by individual nodes, which work as Matcher. Before getting into Waves blockchain, exchange transactions are always checked by the nodes for matching the prices in orders so that the matcher cannot implement the "wrong" transactions. Then the Matcher creates Exchange Transaction, signs it with its signature and puts it into blockchain to fix changes in balances of users. The Matcher also can match orders partially, as at ordinal exchange. After the transaction is confirmed, Matcher's sign is validated by mining nodes and exchange transaction is added to the blockchain, user account balances of tokens are changed according to the amount and order execution price. The important point is that the funds are transferred only after publishing in the blockchain. If the Matcher fails, the exchange will not take place, but the funds will not be lost, because the exchange does not own client's tokens.
# Matching Algorithm
A user initiates his willingness to purchase or sell tokens by creating, signing and sending limit or marker order to the matcher node. For details about limit and market orders, see Order section of the Matcher API article.
The Limit Order in this example is similar to other exchanges: an order for a buy (sell) of a fixed number of a token at a price equal to or better than specified. When a new Order is submitted to WX Network all its fields are checked for adequacy and a signature is validated by the sender's public key. Then, the Order is validated, based on internal Matcher state: Order with such id should not exist already and the sum of all Order amounts for a particular token should be less than or equal to the balance of that token on the sender's account. See flow chart below:
User can set order expiration time (maximum timestamp), and when the order expires it will be automatically canceled. Limit orders older than 30 days are cancelled automatically, while the market orders have no default expiration time. Expiration time is specified when the order is signed. The expiration time is a long integer value that represents the absolute number in milliseconds since the UNIX epoch. When the order is unfilled and its expiration time is more than now UNIX timestamp, it can be canceled by the user. In this case, the order gets into blockchain as Cancelled order and nobody can fill it since then.
Every order has a certain state, depending on the stage of its life cycle. When an order is in the order book, but not filled yet - it has "Accepted" state, also it can be "Filled", "Partially Filled" or "Canceled". Orders, which are not fully filled, can be canceled, after that the order will be removed from the matcher's order book.
# Price Calculation
A new submitted Order is matched against orders in OrderBook if there is such order with price that is better or equal to the submitted one.
- For 'BUY' order better means there is a 'SELL' order with price <= submitted.
- For 'SELL' order better means there is a 'BUY' order with price >= submitted.
Execution price of ExchangeTransaction is always determined by the price of an order that was accepted earlier, i.e. an order that is already in OrderBook.
# Full Execution
- If for a submitted order there is no counter-order matched by price (which price is equal or better) that order would be placed in the corresponding
OrderBookand will remain open until executed or until themaxTimestampis reached. - If there is a counter-order that matches a submitted order then order execution is performed. That means the counter-order is removed from
OrderBookandExchangeTransactionis created and signed by the Matcher's private key and is sent to the Waves network to be included in the blockchain. - If there are multiple orders, that are matched with a new order, the earliest based on acceptance time gets chosen.
# Partial Execution
- If an amount of a submitted order is big enough to execute a few orders, Matcher creates several
ExchangeTransaction. Created transactions have amounts equal to matched counter-order amounts. Matched counter-orders are chosen in order of their acceptance time (First In, First Out). - If after the execution of all counter-orders at a particular price there is still remaining amount from the submitted order, the next price level of
OrderBook, which satisfy the incoming price, is used to execute orders. For all matched counter-orders correspondingExchangeTransactionare created similarly to the previous step. - If after all matches found on the previous steps there is still remaining amount from the submitted order and there are no other open orders matched by the price, a new
Orderis put onOrderBookwith remaining amount out of initialOrder. - If the first matched order in
OrderBookhas an amount greater than the submitted one,ExchangeTransactionwill be created with amount equals to the incoming order. Partially executed counter-order will be substituted with remaining amount inOrderBook.
# Matcher Fee Calculation
See Matcher Fee.
# Tradable Balance
Tradable balance shows, how much you can spend in orders. It is calculated by the formula:
tradable_balance(asset) = balance_of_asset -
spendings_of_asset_in_transactions_in_utx_pool -
reserved_balance_for_asset
# balance_of_asset
The current balance in asset:
- WAVES;
- assets.
# Spendings of Asset in Transactions in UTX Pool
The sum of all spendings by the asset of unconfirmed transactions.
For example, if you are transferring WAVES and sending a data transaction
and these transactions haven't yet forged, spendings_of_WAVES_in_transactions_in_utx_pool will be amount_of_transferred_waves + transfer_fee + data_transaction_fee.
Note: UTX pool of one node could not be the same as on other node.
# Reserved Balance for Asset
Also known as open volume. The sum of all spending by the asset of all orders in pairs with this asset.
For example, you buy BTC by Bitcoin Cash (1) and sell Bitcoin Cash for WCT (2), and these orders are still active and haven't filled yet.
Then spendings_of_Bitcoin_Cash_in_active_orders will be amount_of_spending_Bitcoin_Cash in (1) + amount_of_selling_Bitcoin_Cash in (2).
Note: For WAVES the order's fees are included in reserved balance.
As you know, all orders in WX Network require WAVES as the fee. Because of this, there is an exception for the rule we spoke above.
If you buy WAVES by other asset, reserved balance in waves in this order will be: max(fee - amount_of_received_waves_in_this_order, 0).
So, you can buy WAVES for BTC even if you have no WAVES.